Google Search Console (GSC) is an indispensable tool for SEO as it provides data about the organic performance of a website or page. Understanding how users search for products and services, measuring your site performance in search engines, and getting recommendations for improvements are vital to SEO. Originally known as Google Webmaster Tools, GSC is the SEO tool that most professionals either use or should be using for insights and technical health.
What Is Google Search Console (GSC)?
GSC is a free service from Google that allows site owners to monitor their overall site health and performance using data directly from Google. It offers several valuable reports, including:
- Impressions and Clicks
- Indexation
- Links
- Manual Actions
- Core Web Vitals (CWV)
GSC also allows site owners to take actions related to their site like submitting a sitemap, removing URLs from the index, and inspecting URLs for any indexing issues. Additionally, GSC regularly sends updates via email to verified owners and users indicating any crawl errors, accessibility issues, or performance problems.
How To Get Started With GSC
To get started with Google Search Console, you’ll need a working Google account (such as a Gmail account or an email account associated with a Google Workspace for business) and the ability to add code to your website or update the domain name servers with your hosting provider. Here are the steps to get started:
Verifying Site Ownership
1. Go to the Google Search Console page.
2. Click on Start Now.
3. Select the type of property you want to verify: Domain or URL Prefix.
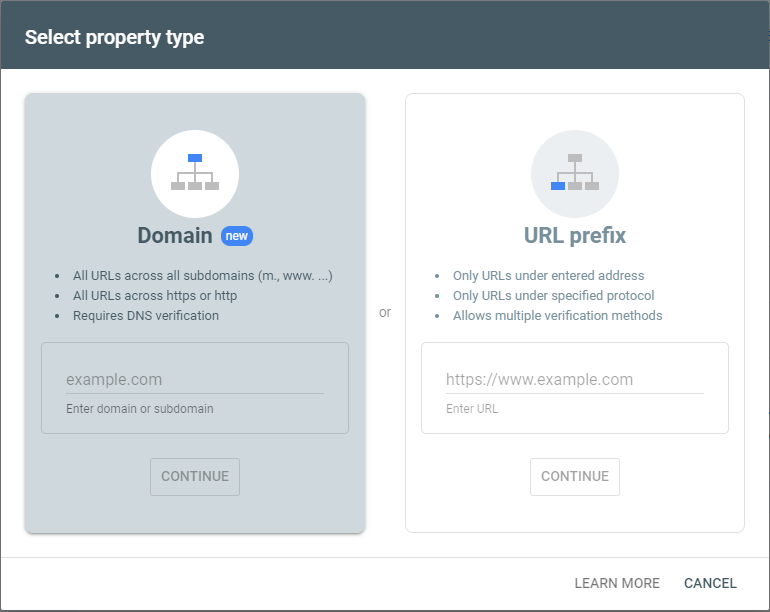
Domain Verification:
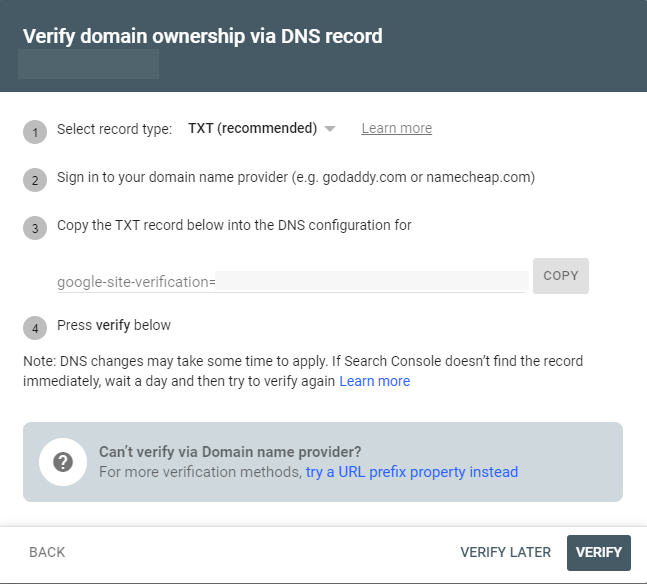
TXT Verification (Preferred):
- Copy the text in the TXT record field.
- Create a new DNS record for your domain with the Type set to TXT.
- Paste the verification TXT from GSC into the Record field and save.
- Click Verify in GSC to verify the TXT record.
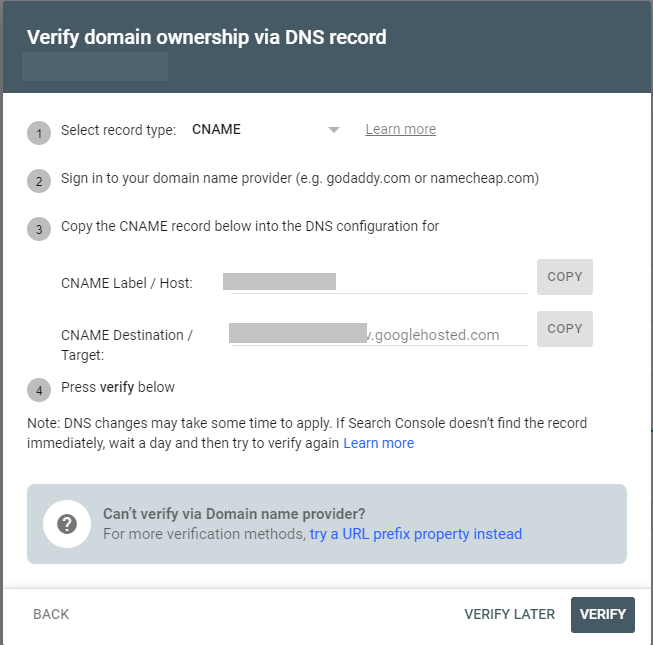
CNAME Verification:
- Copy the CNAME label and paste it into the Name field of a new CNAME record.
- Copy the CNAME Destination/Target content into the Record field and save.
- Click Verify in GSC to verify the CNAME record.
Watch this video by Google for more details:
Once you have verified your domain, you can verify additional properties for this domain using the URL Prefix property type.
URL Prefix Verification:
- HTML Page: Upload the .html file directly to your site’s root directory.
- HTML Tag: Add the provided HTML tag to your homepage’s <head> section.
- Google Analytics: Use your Google Analytics verification.
- Google Tag Manager: Use your Google Tag Manager tags for verification.
- DNS Configuration: Use the TXT or CNAME methods described above for sub-sections.
Adding a Sitemap in GSC
To add a sitemap to GSC:
- Go to the sitemap URL you want to add and copy the URL – https://www.domain.com/sitemap.xml
- In GSC, click on Sitemaps in the left column.
- Add your sitemap URL in the Add a new sitemap field and click Submit.
Setting Users, Owners, and Permissions
Control access to GSC by setting permissions:
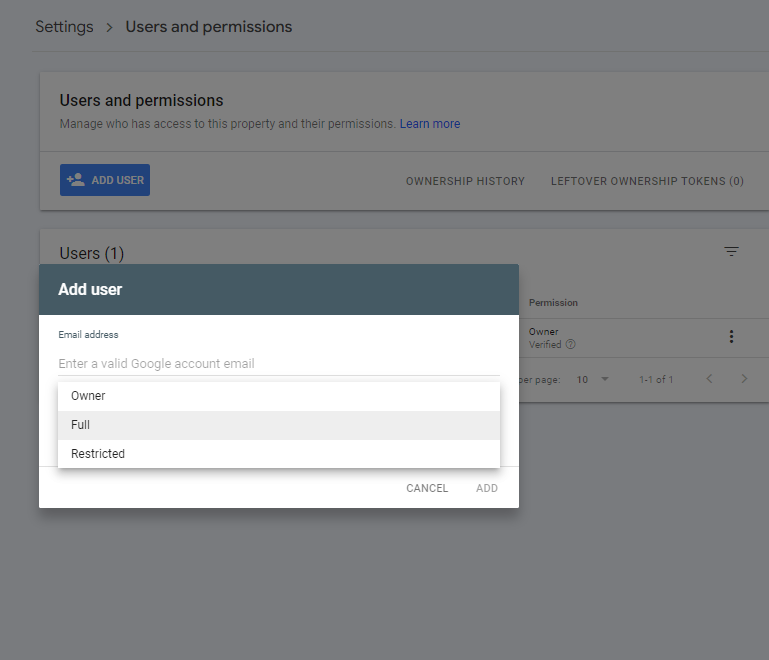
- Owner: Full control over the property, including complete removal.
- Full User: Access to almost all functions but can’t remove the property entirely.
- Restricted User: Can only view the data without making changes.
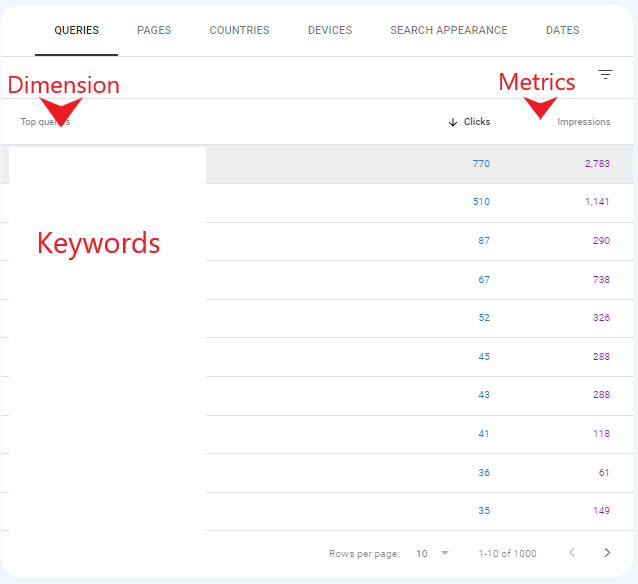
Dimensions and Metrics
GSC data is segmented into Dimensions and Metrics. In the Performance report, Dimensions group data into meaningful segments, such as Pages, Queries, Countries, and Devices. Metrics include data such as Impressions and Clicks.
Troubleshooting with GSC
Crawling Issues
Long before a page can rank in the search engines, it needs to be crawled and then indexed. A page must be crawlable to be evaluated for search.
- Fetching robots.txt files.
- Resolving DNS.
Connecting to servers.To use this report:
- Click on Settings in the left column of GSC.
- Click on Open Report next to Crawl Stats in the Crawling section of the Settings page.
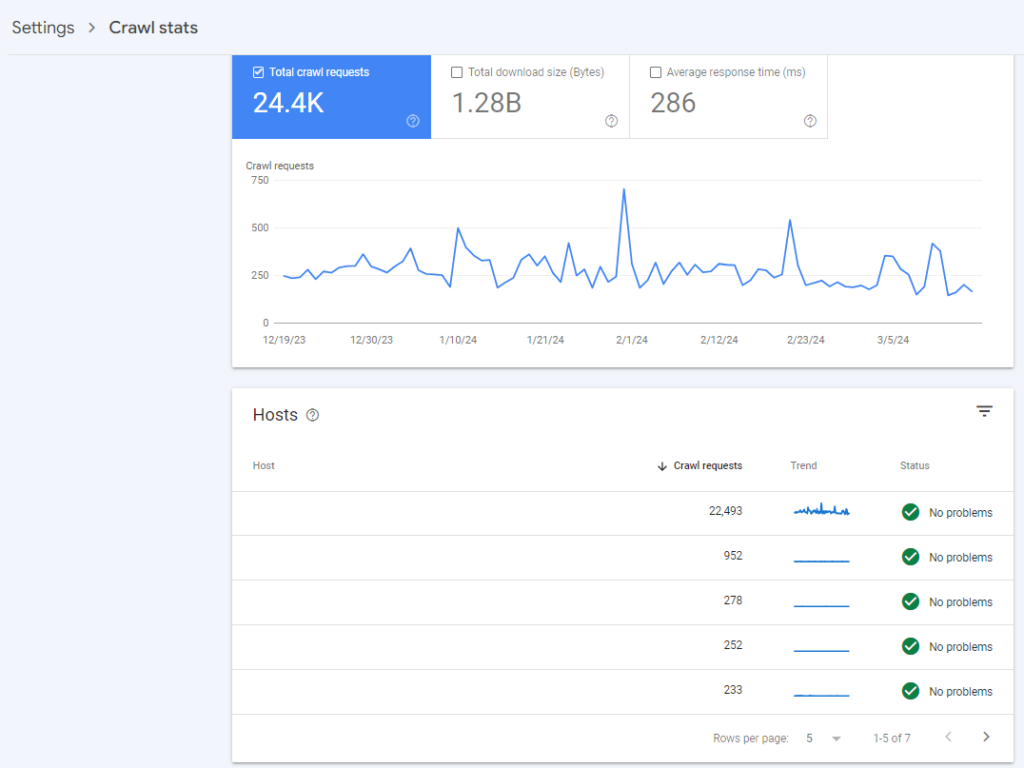
- Review the Hosts section of the page to see if any of your subdomains are experiencing problems,
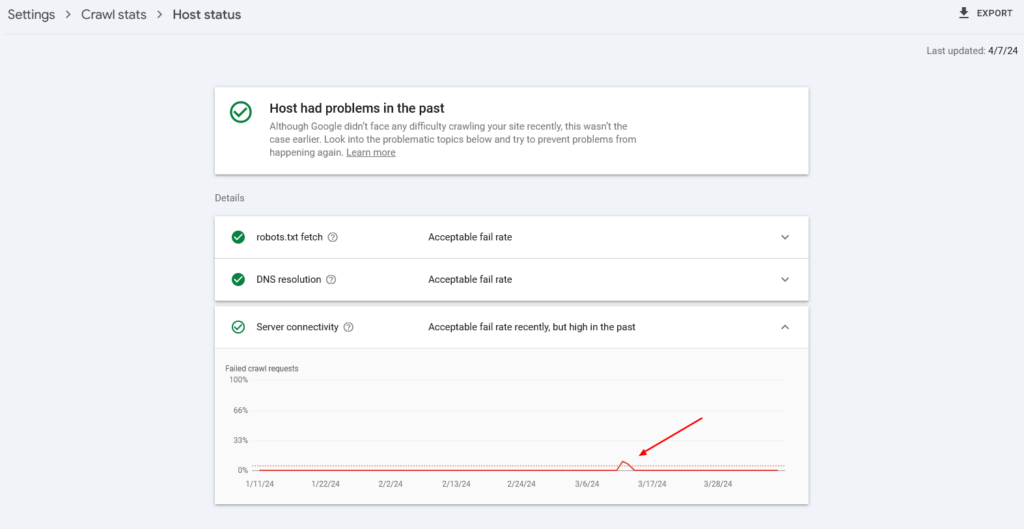
- If your host has experienced issues in the past, you will see a fail rate report.
- Review the By response section of the page to see what percentage of pages crawled result in suboptimal response codes.
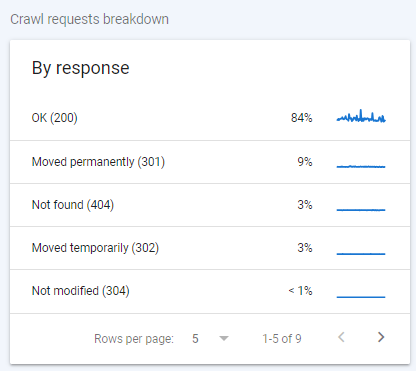
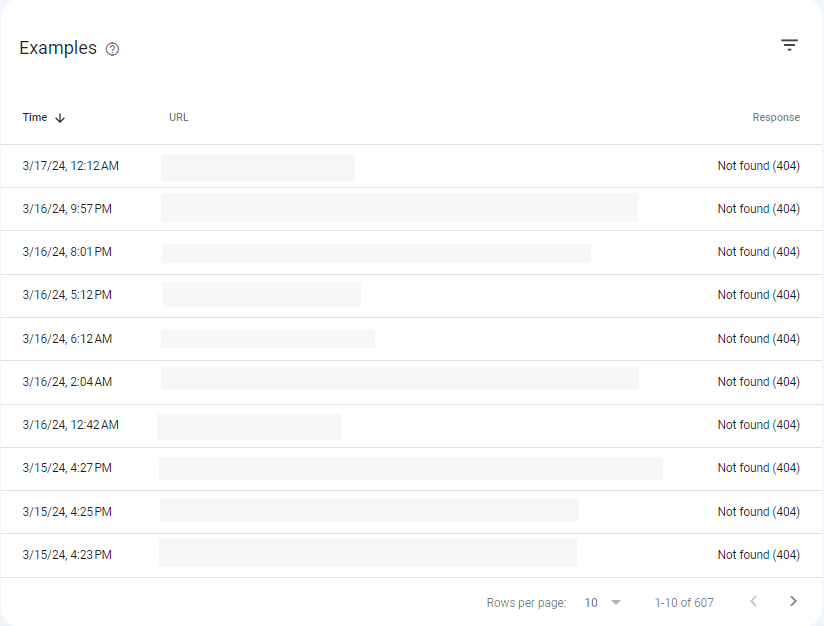
If there are any pages with 404 response codes, click on Not found to review these pages.
Indexation Issues
To see which pages on your site are not being indexed:
- Click on Sitemaps in the left column of GSC.
- Click on the three vertical dots next to your site’s primary sitemap and select See page indexing.
- Select See page indexing.
The resulting report is like the Pages report, but it focuses on pages your site has outlined as important enough to include in the sitemaps you have submitted to Google.
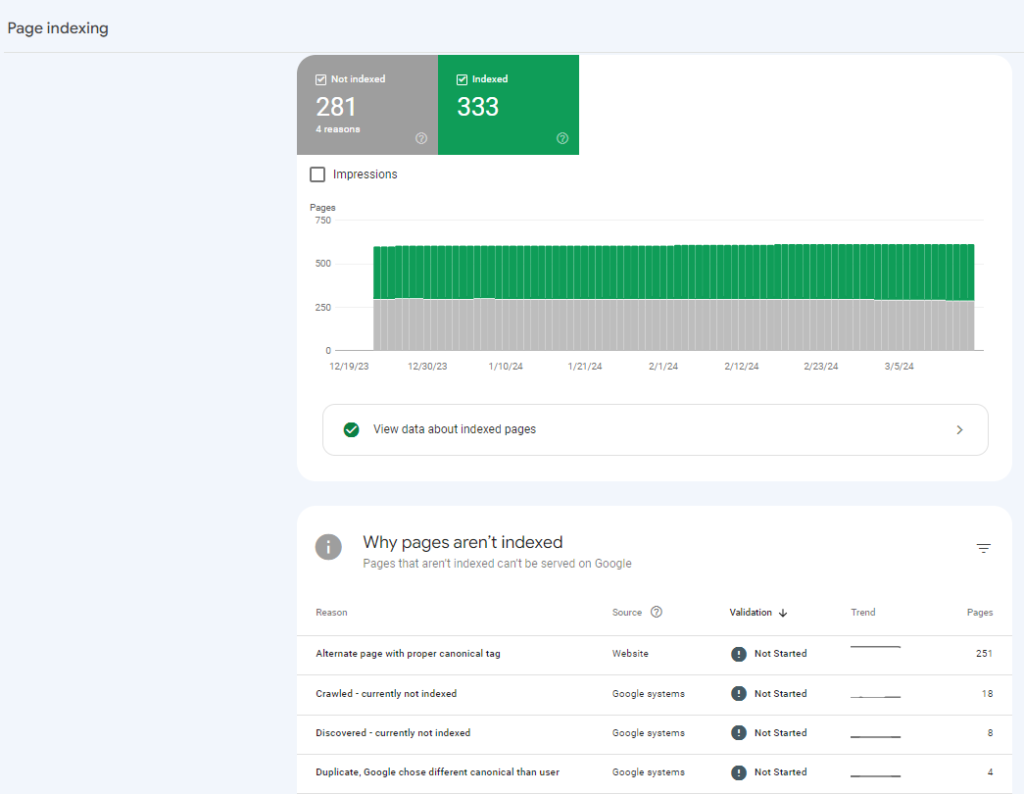
From here, you can review the Reasons columns in the “Why pages aren’t indexed” table.
For example, you may have several pages that have been Crawled but are currently not indexed. To evaluate one of the pages, do the following:
- Click on the Crawled – currently not indexed line item to see the list of pages.
- Hover over one of the pages listed until three icons appear after the URL.
- Click on the Inspect URL icon.
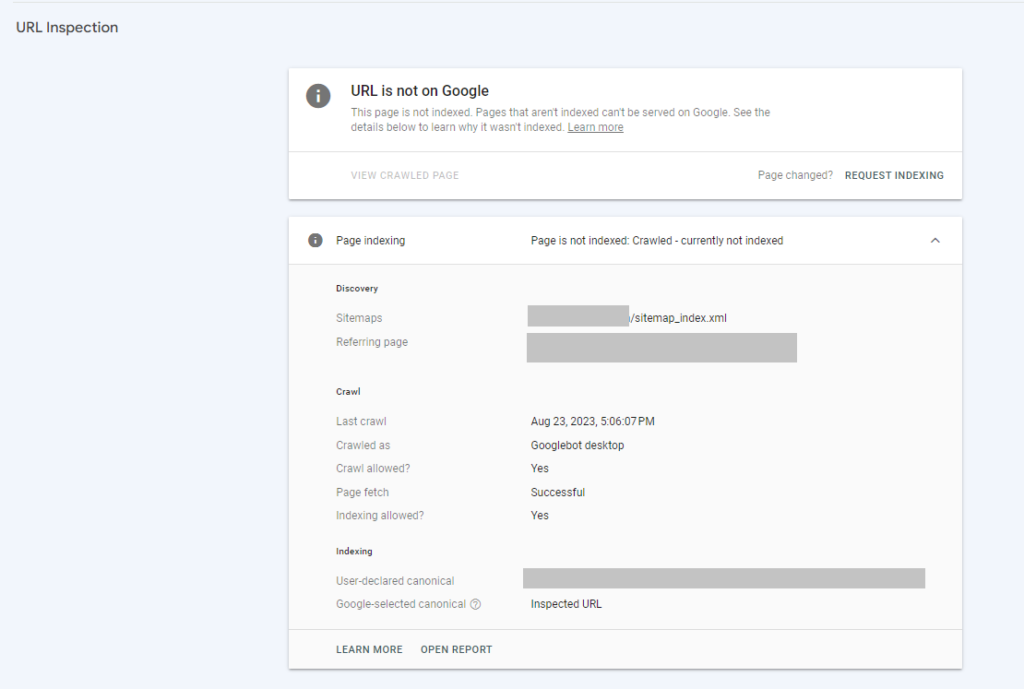
- From this page, you can Request Indexing manually.
- You can also click on the “TEST LIVE URL” button on the right side of the page.
- The resulting page will indicate whether or not your page is available to Google.
- To view the test results for the page, click on View Tested Page.
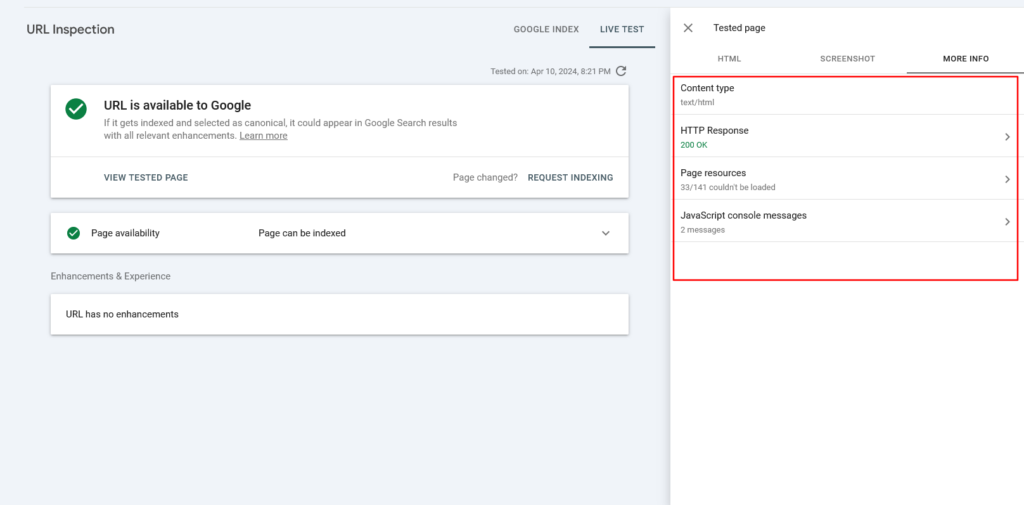
- The resulting pop-in window shows the HTML captured from the page, a smartphone rendering of the page, and “More Information” on the page, including any page resource issues or JavaScript console errors.
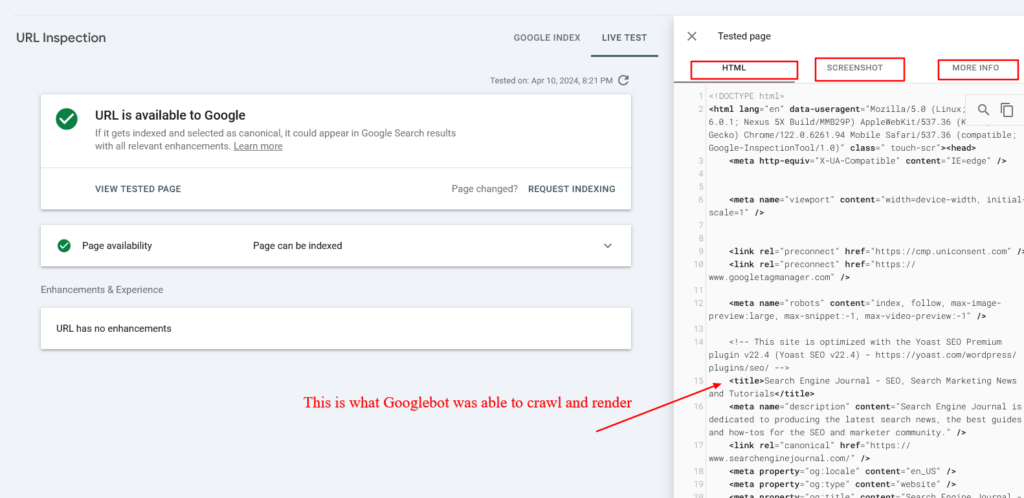
Rendered HTML by Googlebot
The HTML code displayed in the inspection tool reflects what Googlebot could crawl and render, which is especially crucial for JavaScript-based websites where the content does not initially exist within the static HTML but is loaded via JavaScript (via REST API OR AJAX).
By examining the HTML, you can determine if Googlebot could properly see your content. If your content is missing, it means Google couldn’t crawl your webpage effectively, which could negatively impact your rankings.
By checking the “More Information” tab, you can identify if Googlebot could not load certain resources. For example, you may be blocking certain JavaScript files that are responsible for loading content via robots.txt.
If everything appears in order, click Request Indexing on the main URL inspection page. The field at the top of every page in GSC allows you to inspect any URL on your verified domain.
I would also recommend making sure Google doesn’t have issues when crawling robots.txt under Settings > robots.txt. If you have a robots.txt and Google isn’t able to fetch it ( for example, because of a firewall blocking access), then Google will temporarily stop crawling your website for 12 hours. If the issue is not fixed, it will behave as if there is no robots.txt file.
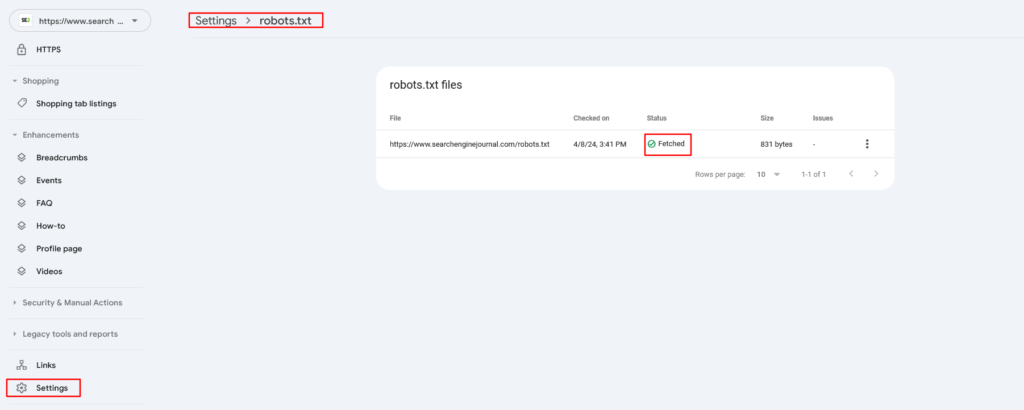
Robots.txt Setting in Search Console
Performance Issues
Review Core Web Vitals (CWV) across your site. CWV measures three major usability metrics:
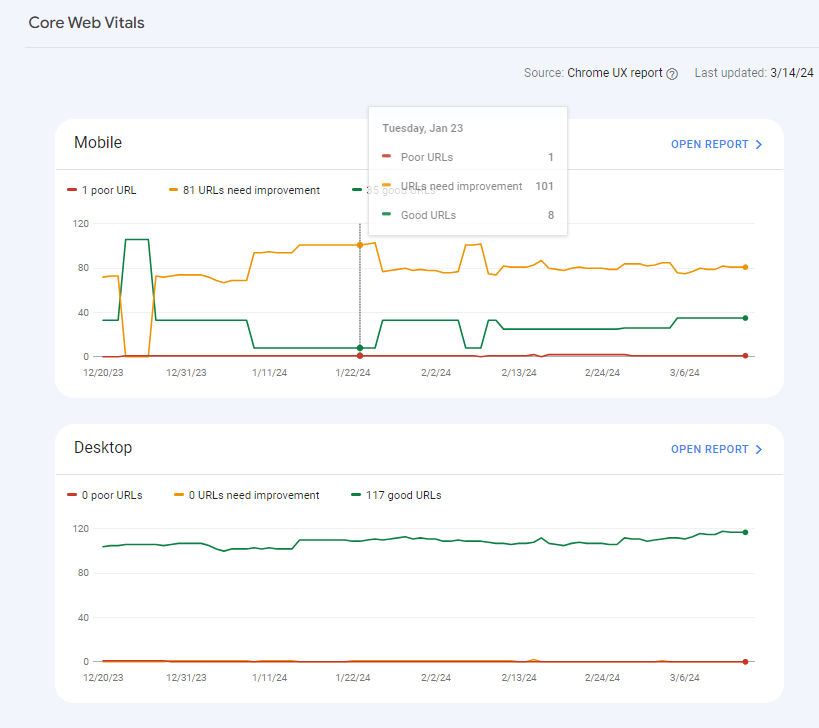
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
To see the issues your pages may have:
- Click on Core Web Vitals in the left column of GSC.
- Click on Open Report in either the Mobile or the Desktop graph.
- Click on one of the line items in the Why URLs aren’t considered good table.
- Click on an Example URL.
- Click on the three vertical dots next to one of the Example URLs in the pop-in window.
- Click on Developer Resources – PageSpeed Insights.
- The resulting page will allow you to see Diagnostics of issues that could be affecting your CWV.
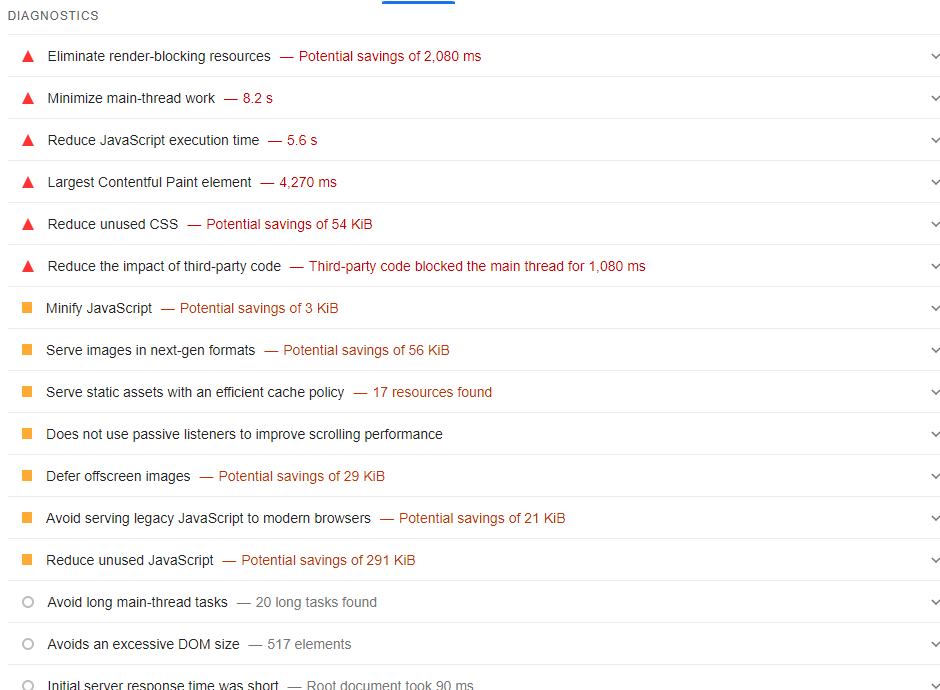
Use these diagnostics to inform your developers, designers, and engineers, who can help you resolve those issues.
Tip: Make sure your website is using HTTPS since it improves your website security and is also a ranking factor. This is quite easy to implement because nowadays, almost all hosting providers provide free SSL certificates that can be installed with just one click.
Security and Manual Actions
If you are experiencing issues with indexation and ranking, check the Security and Manual Actions reports.
Using GSC for SEO
1. Measuring Site Performance
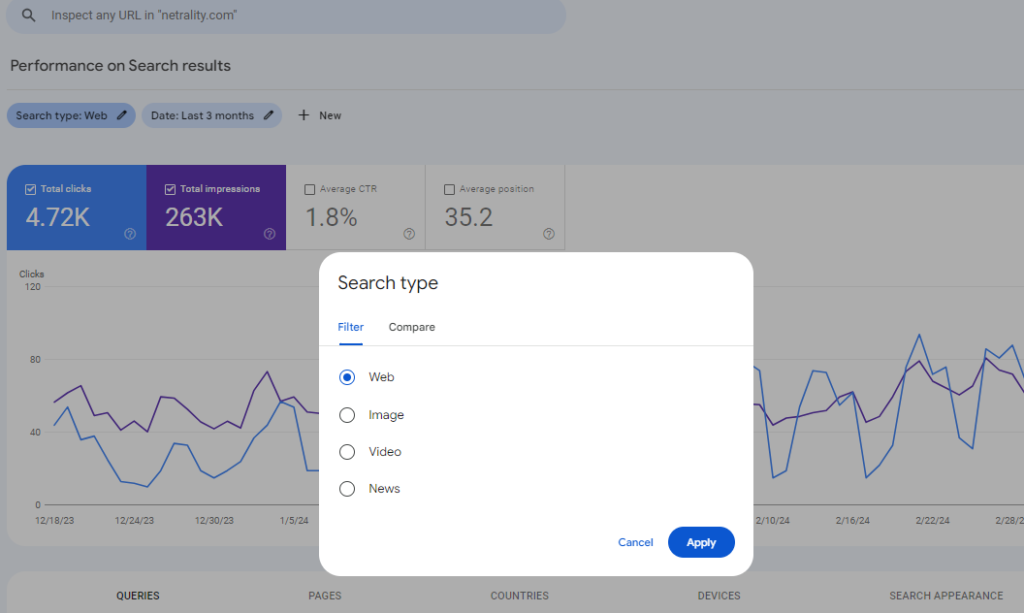
Four search types can be explored in the Performance Report:
- Web.
- Image.
- Video.
- News.
By default, the Search Console shows the Web search type.
Change which search type is displayed by clicking the Search Type button:
The Performance Report provides insights on how a site performs in search. Key metrics include:
- Total Clicks
- Total Impressions
- Average CTR (click-through rate)
- Average Position
2. Finding “Striking Distance” Keywords
The Search results report in the Performance section of GSC allows you to see the Queries and their average Position.
While most queries for which many companies rank in the top three in GSC are branded terms, the queries that fall in the five to 15 rank are considered “striking distance” terms.
You can prioritize these terms based on impressions and refresh your content to include those queries in the language of those pages.
To find these terms:
- Click on Performance in the left column of GSC.
- Click on Search results.
- Total clicks and Total impressions will be enabled by default, so click on Average position to enable that metric as well
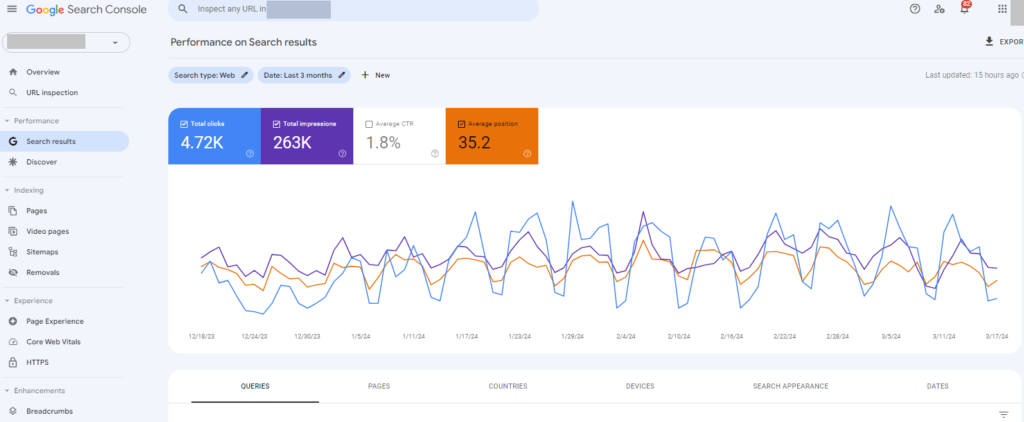
- In the Queries table below, sort the columns by Position and click forward until you get to position 5 through 15.
- Capture the queries that have higher impressions and use these to edify your content strategy.
3. Requesting Faster Indexation of New Pages
For many sites, Googlebot is very efficient and discovers new pages quickly. However, if you have a priority page that you need indexed in a hurry, you can use the URL Inspection tool to test the live URL and then request indexing.
To request indexing:
- Click on URL inspection in the left column of GSC.
- Paste the URL of the page you want indexed into the top search box.
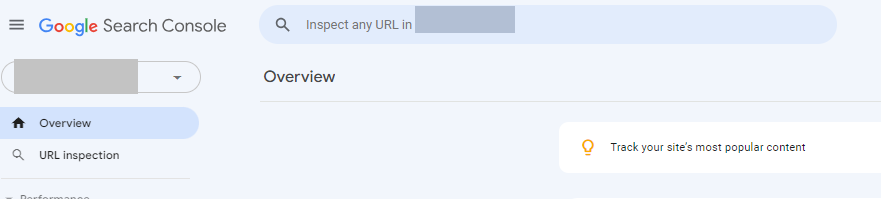
- Hit <Enter>.
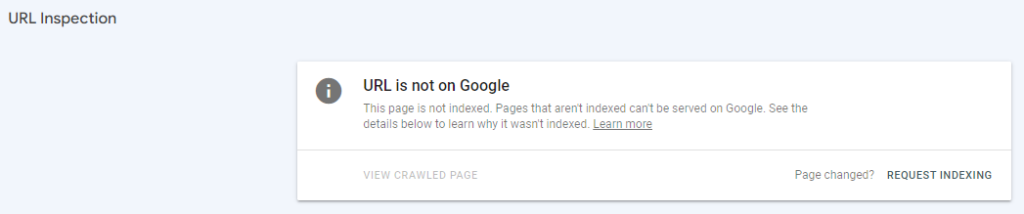
- On the subsequent URL Inspection page, click Request indexing.
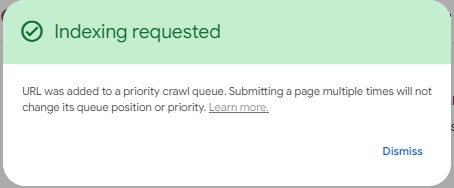
This process will add your URL to Googlebot’s priority queue for crawling and indexing; however, this process does not guarantee that Google will index the page.
If your page is not indexed after this, further investigation will be necessary.
Note: Each verified property in GSC is limited to 50 indexing requests daily.
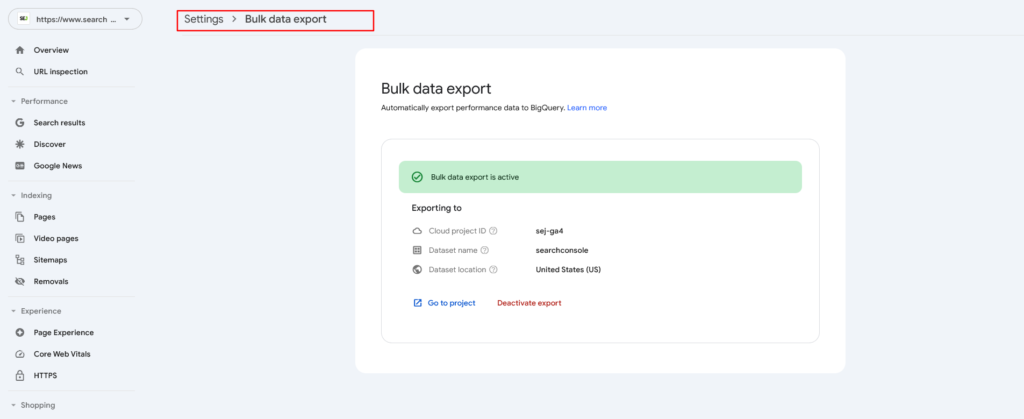
4. Bulk Data Export
GSC historical data are limited to a maximum of 16 months. Fortunately, you can overcome this issue by exporting GSC data into BigQuery, where it can be stored indefinitely. This allows you to access as much historical data as you desire. Since this action is not retroactive, you should start as soon as possible.
5. Bonus: Integration With Other SEO Tools
While you can do many things within GSC, some real magic happens when you integrate the data within GSC into the many SEO tools and platforms available on the market.
Integrating GSC into these tools gives you a sharper view of your site’s performance and potential.
From desktop crawlers, like Screaming Frog and Sitebulb, to enterprise server-driven crawlers, like Lumar and Botify, integrating your GSC information can result in a more thorough audit of your pages, including crawlability, accessibility, and page experience factors.
Integrating GSC into large SEO tools, like Semrush and Ahrefs, can provide more thorough ranking information, content ideation, and link data.
Additionally, the convenience of having all your data in a single view cannot be overstated. We all have limited time, so these options can greatly streamline your workload.
Conclusion
Google Search Console is an essential tool for any SEO professional. It provides valuable insights into your site’s performance, helps you identify and troubleshoot issues, and offers tools to improve your site’s visibility and rankings. By leveraging GSC’s features, you can enhance your SEO strategy and achieve better results in search engine rankings.
More resources:
